What Are Semiconductors? Its Types
Semiconductors are materials whose electrical conductivity is intermediate between conductors (such as metals) and insulators (such as glass). Semiconductors are critical materials of electronic equipment, making everything from computers and smartphones to medical devices and automobiles work. The unique ability property of semiconductors to manage electrical current positions them as the cornerstone of modern technology.
Types of Semiconductors
- Intrinsic Semiconductors: These are pure semiconductor materials, like silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), with no impurities.
- Extrinsic Semiconductors: These are semiconductors that have been doped with impurities intentionally to enhance their conductivity. They are divided further into:
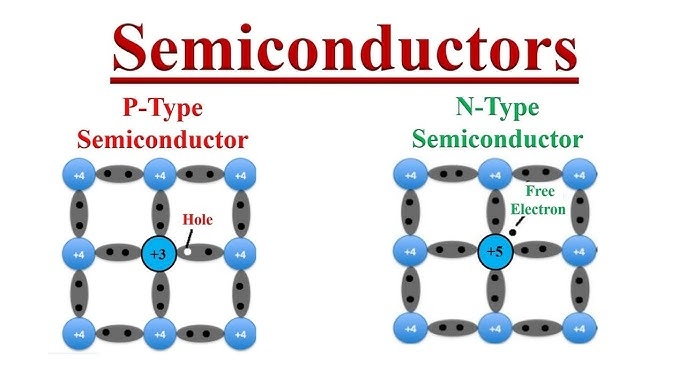
- P-Type Semiconductors: Doped with elements that introduce holes (lack of electrons), with holes as the majority charge carriers.
- N-Type Semiconductors: Doped with elements that introduce additional electrons, with electrons as the majority charge carriers.
How Do Semiconductors Work?
Semiconductors pass electricity by permitting electrons to travel between the valence band and the conduction band. They possess a full valence band and empty conduction band in their native form and therefore are not good conductors. When voltage or heat is externally applied, the electrons acquire energy and move into the conduction band, making controlled electrical conductivity possible. This property is also improved through doping, in which impurities are introduced to form n-type (additional electrons) or p-type (electron holes) semiconductors. When the two types are mixed, engineers create critical semiconductor devices that fuel today’s electronics.
Key Semiconductor Components

- Diodes: These devices permit electric current to pass in a single direction only, and hence they are crucial in rectifiers, LED lights, and power supply circuits. A standard diode is a p-n junction, where the n-type and p-type semiconductors’ meeting creates a barrier that regulates current flow.

- Transistors: These are the constituents of contemporary electronic circuits, used as switches or amplifiers. In switch mode, transistors regulate the passage of electrical signals, facilitating binary operations in computers. As amplifiers, they amplify feeble signals, making them vital in audio and radio communications.

- Integrated Circuits (ICs): ICs are compact electronic circuits comprising numerous transistors, diodes, resistors, and capacitors in one semiconductor chip. They carry out advanced functions like data processing, signal amplification, and memory storage, making it possible to use smartphones, computers, medical equipment, and industrial automation systems.
Impact of Semiconductors on Different Industries
Semiconductors power technology innovation in numerous industries, leading to efficiency, automation, and intelligent systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Semiconductors power smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, and home appliances. They enhance processing speed, energy efficiency, and connectivity, making devices smarter and more interactive.
- Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles rely on semiconductors for automation, safety, and performance. They control ECUs, infotainment systems, ADAS, and EV battery management, driving advancements in connected and autonomous cars.
- Healthcare & Medical Technology: Semiconductors enable medical imaging (MRI, CT scans), wearable trackers, robotic surgeries, and pacemakers. They support real-time data analysis, remote monitoring, and precise diagnostics, improving healthcare efficiency.
- Telecommunications & Networking: These chips fuel 5G, fiber-optic communication, and satellite technology. They ensure faster data transmission, stable networks, and seamless global connectivity, driving digital transformation.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Internet of Things (IoT): AI, machine learning, and IoT devices depend on semiconductors for high-speed processing and automation. From smart homes to industrial applications, these chips enable fast data handling and improved performance.
Major semiconductor manufacturing facilities in India
- Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL), Chandigarh: This is a government-run facility focused on semiconductor research and production. It plays an important role in developing chips for defense, space, and communication technology.

- ISRO’s Semiconductor Facilities: India’s space agency, ISRO, has its own semiconductor units that produce chips for satellites, space research, and navigation systems, helping India advance in space technology.
- Tata Electronics: Tata Electronics is investing heavily in semiconductor packaging and assembly. By focusing on advanced chip packaging, the company is strengthening India’s role in the global semiconductor supply chain.
- Vedanta-Foxconn Joint Venture (JV): This partnership between Vedanta and Foxconn is setting up India’s first semiconductor fabrication unit, which will help India manufacture its own chips instead of relying on other countries. Vedanta Group has taken full ownership of the joint venture with Foxconn set up last year to manufacture semiconductors in India.

- Mikron and Polymatech: These companies are actively involved in chip production and semiconductor manufacturing, supporting India’s growing demand for locally made semiconductors.
The Future of India’s Semiconductor Industry
India’s semiconductor industry is growing rapidly, driven by government support, local manufacturing, and a rising demand for electronics. As a result, programs like the PLI scheme and the Semicon India Program are attracting investments and encouraging chip production. Moreover, with companies like Vedanta-Foxconn and Tata Electronics setting up manufacturing units, India is steadily moving toward self-reliance in semiconductors. Furthermore, the increasing use of smartphones, 5G, artificial intelligence, and EVs is pushing demand even higher. However, challenges such as infrastructure limitations and high investment costs still exist. Nevertheless, with continuous policy support and active participation from the private sector, India could soon become a major player in the global semiconductor industry.
Conclusion
Semiconductors are the pillars driving technology and innovation in sectors and are the foundation of current times. The semiconductor industry in India is poised for change, with firm government support and growing investments in domestic production. Although there are challenges, the prospects for India look good in achieving its potential as a global semiconductor leader. With continued advancements, the semiconductor industry in India can play a crucial role in shaping the country’s technological and economic growth.